DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) is the standard for the communication and management of medical imaging information. Understanding how to handle DICOM medical imaging data is crucial for healthcare professionals, researchers, and anyone involved in medical imaging. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed overview of DICOM medical imaging data on Mac, including its importance, handling, and best practices.
What is DICOM Medical Imaging Data?
DICOM medical imaging data is a standard for storing, transmitting, and displaying medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and ultrasounds. It includes not only the images themselves but also patient information, image acquisition parameters, and other related data.
DICOM medical imaging data is crucial for healthcare professionals as it allows for the efficient storage, retrieval, and sharing of medical images across different systems and devices. It ensures that medical images are standardized and can be interpreted accurately, leading to better patient care and diagnosis.
Importance of DICOM Medical Imaging Data on Mac
Understanding the importance of DICOM medical imaging data on Mac is essential for healthcare professionals, researchers, and anyone involved in medical imaging. DICOM, which stands for Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine, serves as the standard for the communication and management of medical imaging information. It allows for the storage, transmission, and display of various medical images, including X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and ultrasound images, along with associated patient information and image acquisition parameters. Efficient handling of DICOM data on Mac ensures standardized interpretation and accurate diagnosis, ultimately leading to improved patient care and outcomes. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed overview of the significance of DICOM medical imaging data on Mac and the best practices for its effective utilization.
Handling DICOM Medical Imaging Data on Mac
Handling DICOM medical imaging data on Mac involves utilizing specific software and tools designed to support the DICOM standard. Mac users can leverage dedicated DICOM viewers and specialized medical imaging software to access, analyze, and manage DICOM files seamlessly. Additionally, integrating DICOM-compatible hardware, such as medical image acquisition devices, with Mac systems is essential for ensuring smooth data transfer and compatibility. Understanding the intricacies of DICOM data management on Mac empowers healthcare professionals and researchers to efficiently interpret and share medical images, contributing to improved patient care and diagnostic accuracy. Embracing best practices for handling DICOM medical imaging data on Mac is paramount for maximizing the benefits of this crucial standard in the medical imaging field.
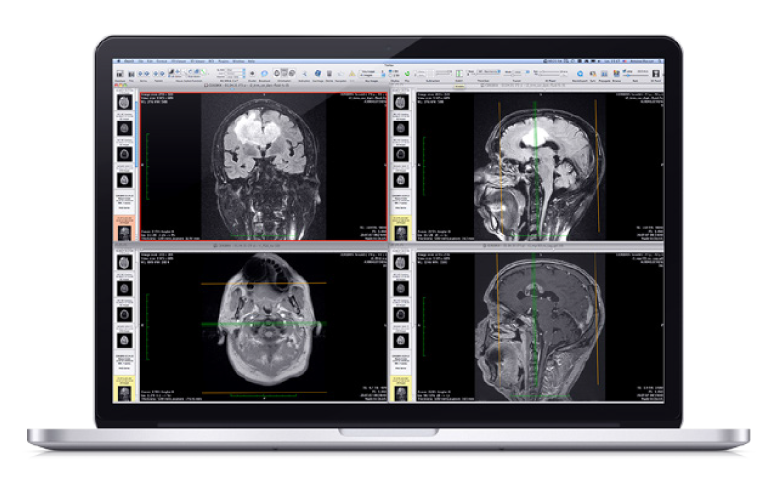
Best Practices for Managing DICOM Medical Imaging Data on Mac
When it comes to managing DICOM medical imaging data on Mac, there are several best practices that healthcare professionals and researchers can follow to ensure efficient handling and analysis. Firstly, it’s crucial to utilize specialized DICOM viewers and software applications designed specifically for Mac OS. These tools offer features such as image viewing, annotation, measurement tools, and integration with other medical software systems, enhancing the overall workflow. Additionally, understanding DICOM standards is essential for Mac users to ensure interoperability with other medical imaging systems and enhance data security. By following these best practices, Mac users can effectively manage and analyze DICOM medical imaging data, ultimately improving patient care and diagnosis.
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively managing DICOM medical imaging data on Mac is essential for healthcare professionals and researchers. By adhering to DICOM standards, utilizing specialized software, and adopting best practices, Mac users can ensure the seamless handling and analysis of medical imaging data, ultimately improving patient care and medical research.


